First Year Engineering Semester 2 Syllabus
First Year Engineering Semester 2 Syllabus – The second semester syllabus for Mumbai University engineering degree course is as bad as the first semester.There are wore subjects like engineering drawing that needs hundreds of hours of practice to clear as well as applied mathematics 2 that is worse than math 1 in many ways.Work extremely hard to avoid an ATKT in this semester.
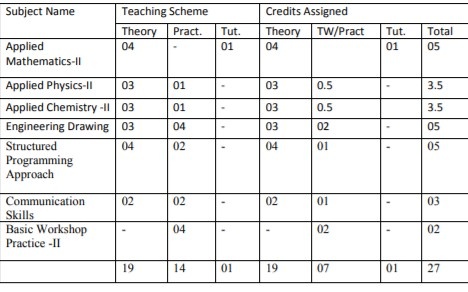
Contents
First Year Engineering Semester 2 Syllabus
APPLIED MATHEMATICS 2
Module?1: Differential Equations of First Order and First Degree
1.1 Exact differential Equations , Equations reducible to exact form by using
integrating factors.
1.2 Linear differential equations(Review), equation reducible to linear form,
Bernoulli’s equation.
1.3: Simple application of differential equation of first order and first degree to
electrical and Mechanical Engineering problem (no formulation of differential
equation)
4 hrs
3 hrs
2 hrs
2
Module?2: Linear Differential Equations With Constant Coefficients and
Variable Coefficients Of Higher Order
2.1. Linear Differential Equation with constant coefficient? complementary
function, particular integrals of differential equation of the type f(D)y = X
where X is ?????? , sin(ax+b), cos (ax+b), ????, ??????V, xV.
2.2. Cauchy’s homogeneous linear differential equation and Legendre’s
differential equation, Method of variation of parameters.
6 hrs.
3 hrs
3
Module?3: Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations of first
order and first degree, Beta and Gamma Function
3.1. (a)Taylor’s series method (b)Euler’s method
(c) Modified Euler method (d) Runga?Kutta fourth order formula (SciLab
programming is to be taught during lecture hours)
3.2 . Beta and Gamma functions and its properties.
4 hrs
4 hrs
4
Module ?4: Differentiation under Integral sign, Numerical Integration and
Rectification
4.1. Differentiation under integral sign with constant limits of integration.
4.2. Numerical integration? by (a) Trapezoidal (b) Simpson’s 1/3rd (c)
Simpson’s 3/8th rule (all with proof). (Scilab programming on (a) (b) (c) (d) is
to be taught during lecture hours)
4.3. Rectification of plane curves.
2 hrs
3 hrs
3 hrs
28
5.
Module?5: Double Integration
5.1. Double integration?definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals.
5.2. Change the order of integration, Evaluation of double integrals by
changing the order of integration and changing to polar form.
2 hrs
7 hrs
6.
Module?5: Triple Integration and Applications of Multiple Integrals.
6.1. Triple integration definition and evaluation (Cartesian, cylindrical and
spherical polar coordinates).
6.2. Application of double integrals to compute Area, Mass, Volume.
Application of triple integral to compute volume.
APPLIED PHYSICS 2
INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION OF LIGHT
Interference by division of amplitude and by division of wavefront; Interference in
thin film of constant thickness due to reflected and transmitted light; origin of
colours in thin film; Wedge shaped film(angle of wedge and thickness
measurement); Newton’s rings
Applications of interference – Determination of thickness of very thin wire or foil;
determination of refractive index of liquid; wavelength of incident light; radius of
curvature of lens; testing of surface flatness; Anti-reflecting films and Highly
reflecting film.
Diffraction of Light –Fraunhoffer diffraction at single slit, Fraunhoffer diffraction at
14 hrs
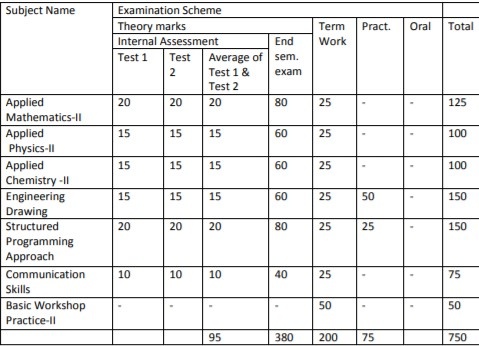
Subject
Code Subject Name
Examination Scheme
Theory
Term
Work Practical Oral Total Internal Assessment End SEM.
Exam. Test
1
Test
2
Average of Test
1 & 2
FEC202 Applied
Physics-II
15 15 15 60 25 – – 100
30
double slit, Diffraction Grating, Resolving power of a grating, dispersive power of a
grating
Application of Diffraction – Determination of wavelength of light with a plane
transmission grating
Module 2 LASERS
Quantum processes as absorption, spontaneous emission and stimulated emission;
metastablestates, population inversion, pumping, resonance cavity, Einsteins’s
equations; Helium Neon laser; Nd:YAG laser; Semiconductor laser,
Applications of laser- Holography (construction and reconstruction of holograms)
and industrial applications(cutting, welding etc), Applications in medical field
04hrs
Module 3 FIBRE OPTICS
Total internal reflection; Numerical Aperture; critical angle; angle of acceptance;
Vnumber; number of modes of propagation; types of optical fiber; Losses in optical
fibre(Attenuation and dispersion)
Applications of optical fibre – Fibre optic communication system; sensors (Pressure,
temperature, smoke, water level), applications in medical field
04 hrs
Module 4 ELECTRODYNAMICS
Cartesian, Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinate system, Scaler and Vector field,
Physical significance of gradient, curl and divergence, Determination of Maxwell’s
four equations.
Applications-design of antenna, wave guide, satellite communication etc.
08 hrs
Module 5 CHARGE PARTICLE IN ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
Fundamentals of Electromagnetism, Motion of electron in electric field (parallel
,perpendicular, with some angle); Motion of electron in magnetic field
(Longitudinal and Transverse); Magnetic deflection; Motion of electron in crossed
field; Velocity Selector; Velocity Filter, Electron refraction; Bethe’s law;
Electrostatic focusing; Magnetostatic focusing; Cathode ray tube (CRT);Cathod ray
Oscilloscope (CRO)
Application of CRO: Voltage (dc,ac), frequency, phase measurement.
05 hrs
Module 6 NANOSCIENCE AND NANOTECHNOLOGY
Introduction to nano-science and nanotechnology, Surface to volume ratio, Two
main approaches in nanotechnology -Bottom up technique and top down technique;
Important tools in nanotechnology such as Scanning Electron Microscope,
Transmission Electron Microscope, Atomic Force Microscope.
Nano materials: Methods to synthesize nanomaterials (Ball milling, Sputtering,
Vapour deposition, solgel), properties and applications of nanomaterials.
APPLIED CHEMISTRY 2
Corrosion:
Introduction: Types of Corrosion- (I) Dry or Chemical Corrosion-i) Due to oxygen ii)
Due to other gases (II) Wet or Electrochemical corrosion- Mechanism i) Evolution of
hydrogen type ii) Absorption of oxygen. Types of Electrochemical Corrosion- Galvanic
cell corrosion, Concentration cell corrosion (differential aeration), Pitting corrosion,
Intergranular corrosion, Stress corrosion. Factors affecting the rate of corrosion- Nature of
metal, position of metal in galvanic series, potential difference, overvoltage, relative area
of anodic and cathodic parts, purity of metal, nature of the corrosion product, temperature,
moisture, influence of pH, concentration of the electrolytes. Methods to decrease the rate
of corrosion- Material selection, Proper designing, Use of inhibitors, Cathodic protectioni)
Sacrificial anodic protection ii) Impressed current method, Anodic protection method,
Metallic coatings- hot dipping- galvanizing and tinning, metal cladding, metal spraying,
Electroplating, Cementation. Organic coatings – Paints (only constituents and their
functions).
11
hrs
Subject
Code Subject Name
Examination Scheme
Theory
Term
Work Practical Oral Total Internal Assessment End SEM.
Exam. Test
1
Test
2
Average of
Test 1 & 2
FEC203 Applied
Chemistry-II
15 15 15 60 25 – – 100
33
Module 2 Alloys
Introduction, purpose of making alloys, Ferrous alloys, plain carbon steel, heat resisting
steels, stainless steels (corrosion resistant steels), effect of the alloying element- Ni, Cr,
Co, Mn, Mo,W and V;
Non-Ferrous alloys- Composition, properties and uses of- Alloys of Aluminium- i)
Duralumin ii) Magnalium. Alloys of Cu- (I) Brasses-i) Commercial brass ii) German
silver, (II) Bronzes- i) Gun metal ii) High phosphorous bronze. Alloys of Pb- i) Wood’s
metal ii) Tinmann’s solder. Powder Metallurgy- Introduction, (1)Methods of powder
metal formation- i) Mechanical pulverization ii) Atomization iii) Chemical reduction iv)
Electrolytic process v) Decomposition (2) Mixing and blending. (3) Sintering (4)
Compacting- i) Cold pressing ii) Powder injection moulding (iii) Hot compaction.
Applications of powder metallurgy.
Shape Memory Alloys- Definition, properties and Uses.
07
hrs
Module 3 Fuels
Definition, classification of fuels-solid, liquid and gaseous. Calorific value- Definition,
Gross or Higher calorific value & Net or lower calorific value, units of heat (no
conversions), Dulong’s formula & numerical for calculations of Gross and Net calorific
values. Characteristics of a good fuel.
Solid fuels- Analysis of coal- Proximate and Ultimate Analysis with Significance and
numericals.
Liquid fuels- Crude petroleum oil, its composition and classification and mining (in
brief). Refining of crude oil- i) Separation of water ii) Separation of ‘S’ & iii) Fractional
Distillation with diagram and composition and uses table.
Cracking- Definition, Types of crackingI)
Thermal cracking – (i) Liquid phase thermal cracking (ii) Vapour phase thermal
cracking. II) Catalytic cracking- (i) Fixed-bed catalytic cracking (ii) Moving-bed catalytic
cracking. Advantages of Catalytic cracking.
Petrol- Refining of petrol, unleaded petrol ( use of MTBE), Catalytic converter, Power
alcohol, Knocking, Octane number, Cetane number, Antiknocking agents.
Combustion- Calculations for requirement of only oxygen and air (by weight and by
volume only) for given solid & gaseous fuels.
Biodiesel- Method to obtain Biodiesel from vegetable oils (Trans-esterification),
advantage and disadvantages of biodiesel.
Fuel cell- Definition, types and applications.
12
hrs
Module 4 Composite Materials
Introduction, Constitution- i) Matrix phase ii) Dispersed phase. Characteristic properties
of composite materials. Classification- (A) Particle – reinforced composites- i) Large –
particle reinforced composites ii) Dispersion – strengthened composites. (B) Fiber –
reinforced composites- i) Continuous – aligned ii) Discontinuous – aligned (short)- (a)
aligned (b) randomly oriented (C) Structural Composites- i) Laminates (ii) Sandwich
Panels.
04
hrs
Module 5 Green Chemistry
Introduction, Twelve Principles of Green chemistry, numerical on atom economy,
Conventional and green synthesis of Adipic acid, Indigo, Ibuprofen and Carbaryl.
Green solvents (ionic liquid supercritical CO2) and products from natural materials.
ENGINEERING DRAWING
Introduction to Engineering Drawing:- Types of Lines, Dimensioning Systems as per IS
conventions.
Engineering Curves: Basic construction of Cycloid, Involutes and Helix (of cylinder) only.
** Introduction to Auto CAD:- Basic Drawing and Editing Commands. Knowledge of
setting up layers, Dimensioning, Hatching, plotting and Printing.
3
36
6) Use CAD tool to draw an isometric view.
**Should be covered during Auto CAD practical sessions.
@ Should be covered only in Term work. (i.e. Questions will not be asked for the End semester
Examination).
Term Work:
Component – 1
Drawing Sheet – 1: Projection of Solids (3 Problems)
Drawing Sheet – 2: Section of Solids and Development of lateral surfaces (2 Problems)
Drawing Sheet – 3: Orthographic Projection without section (2 Problems)
Drawing Sheet – 4: Orthographic Projection with section (2 Problems)
Drawing Sheet – 5: Isometric Views (3 Problems)
Component -2
One A-3 size sketch book consisting of:-
1) 2 problems each from Engineering Curves, Projection of Lines, Planes and Solids.
2) 2 problem from Section of solids and 1 problem from section of solids with Development of
lateral surface of that sectioned Solid.
2
Projection of Points and Lines:- Lines inclined to both the Reference Planes (Excluding
Traces of lines) and simple application based problems on Projection of lines.
@Projection of Planes:- Triangular, Square, Rectangular, Pentagonal, Hexagonal and
Circular planes inclined to either HP or VP only. (Exclude composite planes)
6
3
Projection of Solids: – (Prism, Pyramid, Cylinder, Tetrahedron, Hexahedron and Cone only)
Solid projection with the axis inclined to HP and VP. (Exclude Spheres, Composite, Hollow
solids and frustum of solids). Use change of position or Auxiliary plane method
Section of solids:- Section of Prism, Pyramid, Cylinder, Tetrahedron, Hexahedron & Cone
t b l di l t t l t f l ( E l d C d S ti Pl )
14
4
Orthographic projections:-
• Different views of a simple machine part as per the first angle projection method
recommended by I.S.
• Full or Half Sectional views of the Simple Machine parts
12
Isometric Views: Isometric View/Drawing of blocks of plain and cylindrical surfaces using
plain/natural scale only. (Exclude Spherical surfaces).
• **Drawing of Isometric views using Auto CAD.
• @Reading of Orthographic Projections. [Only for Practical Exam (AutoCAD)
and TW
STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING APPROACH
1.1 Basics of Computer:
Turing Model, Von Neumann Model, Basics of Positional
Number System, Introduction to Operating System and component
of an Operating System.
1.2 Algorithm & Flowchart :
Three construct of Algorithm and flowchart: Sequence, Decision
(Selection) and Repetition
06
2 Fundamentals of
C-Programming
2.1 Character Set, Identifiers and keywords, Data types, Constants,
Variables.
2.2 Operators-Arithmetic, Relational and logical, Assignment,
Unary, Conditional, Bitwise, Comma, other operators.
Expression, statements, Library Functions, Preprocessor.
2.3 Data Input and Output – getchar( ), putchar( ), scanf( ), printf( ),
gets( ), puts( ), Structure of C program .
06
39
3 Control
Structures
3.1 Branching – If statement, If-else Statement, Multiway decision.
3.2 Looping – while , do-while, for
3.3 Nested control structure- Switch statement, Continue statement
Break statement, Goto statement.
12
4 Functions and
Parameter
4.1Function -Introduction of Function, Function Main, Defining a
Function, Accessing a Function, Function Prototype, Passing
Arguments to a Function, Recursion.
4.2 Storage Classes –Auto , Extern , Static, Register
06
5
Arrays , String
Structure and
Union
5.1 Array-Concepts, Declaration, Definition, Accessing array
element, One-dimensional and Multidimensional array.
5.2 String- Basic of String, Array of String , Functions in String.h
5.3 Structure- Declaration, Initialization, structure within structure,
Operation on structures, Array of Structure.
5.4 Union – Definition , Difference between structure and union ,
Operations on a union
14
6 Pointer and
Files
6.1 Pointer :Introduction, Definition and uses of Pointers, Address
Operator, Pointer Variables, Dereferencing Pointer, Void Pointer,
Pointer Arithmetic, Pointers to Pointers, Pointers and Array, Passing
Arrays to Function, Pointers and Function, Pointers and two
dimensional Array, Array of Pointers, Dynamic Memory Allocation.
6.2 Files: Types of File, File operation- Opening, Closing, Creating,
Reading, Processing File