SRMJEE PG Mtech syllabus and model questions
SRMJEE PG Mtech syllabus and model questions – The post graduate entrance test for MTech aspirants at SRM University is called as SRMJEE.Even the undergraduate courses need an entrance exam to get selected into the university and confirm a seat.There are 12 branches of engineering that can be applied for and the syllabus of each branch is also mentioned.There is a 100 questions sample model paper also attached for the post graduate syllabus course.

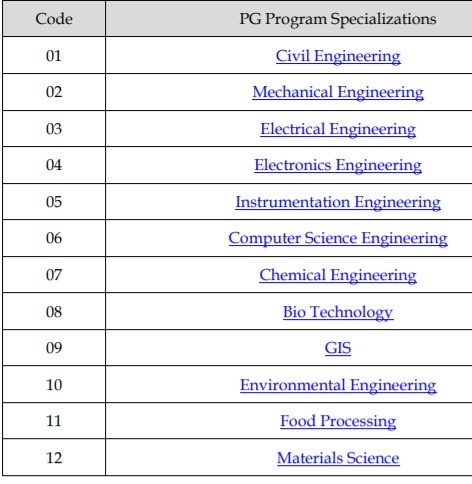
SYLLABUS for SRMJEE M.Tech
Civil (Code 01)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Mechanics of Solids and Structural Analysis
(ii) Construction and Materials Management
(iii) Concrete and Steel Structure
(iv) Soil Mechanics and Geo Technical Engineering
(v) Fluid Mechanics and Water Resources Engineering
(vi) Environmental Engineering
(vii) Surveying
(viii) Transportation Engineering
(ix) Remote Sensing
(x) Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Mechanical (Code 02)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Mechanics and Machine Design
(ii) Material Science and Metallurgy
(iii) Thermo dynamics
(iv) Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
(v) Production Technology
(vi) Automotive Engines
(vii)Automotive Transmission
(viii) Strength of Materials
(ix) Casting, metal forming and metal joining processes
(x) Tool Engineering, Machine tool operation, Metrology and inspection
(xi) Engineering Materials, Processing of Plastics and Computer Aided Manufacturing
(xii) Product Design, Process Planning, Cost Estimate, Design of Jigs and Fixtures and Press Tools
(xiii) Operations Research
(xiv) Operations Management
(xv)Quality Control Reliability and Maintenance
Electrical (Code 03)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Networks : Circuit Elements, Laws and theorems – Resonance – Coupled circuits – AC steady
state and Transient Analysis
(ii) Devices : Energy bands, Charge carriers in semiconductors – semiconductor junctions –
semiconductor diodes and its types – transistors – FET – SCR – IGBT – DIAC – TRIAC – UJT –
Power supplies
(iii) Electronic Circuits : Biasing methods and small signal models – Transistor amplifier and
analysis – Feedback amplifiers and oscillators – Large signal and tuned amplifiers –
Frequency response and wave shaping circuits
(iv) Digital : Number systems – Boolean algebra – Logic gates – Logic families – Gate level
minimization and combinational logic – Synchronous and Asynchronous sequential logic –
Memory
(v) Microprocessor : Intel 8085 microprocessor – Intel 8086/8088 microprocessor – Intel
8031/8051 microcontroller – Programmable interfacing devices – Applications
(vi) Control System : Transfer function – Mathematical Modeling – Block diagram reduction –
Control system components – Transient and steady state analysis – Stability analysis –
Frequency domain analysis
(vii) Electromagnetics
(viii) Electrical Machin
Electronics (Code 04)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Networks :Circuit Elements, Laws and theorems – Resonance – Coupled circuits – AC steady
state and Transient Analysis
(ii) Devices : Energy bands, Charge carriers in semiconductors – semiconductor junctions –
semiconductor diodes and its types – transistors – FET – SCR – IGBT – DIAC – TRIAC – UJT –
Power supplies
(iii) Electronic Circuits : Biasing methods and small signal models – Transistor amplifier and
analysis – Feedback amplifiers and oscillators – Large signal and tuned amplifiers –
Frequency response and wave shaping circuits
(iv) Digital : Number systems – Boolean algebra – Logic gates – Logic families – Gate level
minimization and combinational logic – Synchronous and Asynchronous sequential logic –
Memory
(v) Microprocessor : Intel 8085 microprocessor – Intel 8086/8088 microprocessor – Intel
8031/8051 microcontroller – Programmable interfacing devices – Applications
(vi) Control System : Transfer function – Mathematical Modeling – Block diagram reduction –
Control system components – Transient and steady state analysis – Stability analysis –
Frequency domain analysis
(vii) Signals and Systems
(viii) Communications (Analog)
(ix) Communications (Digitals)
(x) Electromagnetics
Instrumentation (Code 05)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Networks: Circuit Elements, Laws and theorems – Resonance – Coupled circuits – AC steady
state and Transient Analysis
(ii) Devices: Energy bands, Charge carriers in semiconductors – semiconductor junctions –
semiconductor diodes and its types – transistors – FET – SCR – IGBT – DIAC – TRIAC – UJT –
Power supplies
(iii) Electronic Circuits : Biasing methods and small signal models – Transistor amplifier and
analysis – Feedback amplifiers and oscillators – Large signal and tuned amplifiers –
Frequency response and wave shaping circuits
(iv) Digital : Number systems – Boolean algebra – Logic gates – Logic families – Gate level
minimization and combinational logic – Synchronous and Asynchronous sequential logic –
Memory
(v) Microprocessor : Intel 8085 microprocessor – Intel 8086/8088 microprocessor – Intel
8031/8051 microco
Computer Science (Code 06)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Discrete Mathematical Structures
(ii) Micro Processor and Hardware Systems
(iii) Computer Organization and Architecture
(iv) System Programming including Assemblers, Compilers
(v) Operating Systems
(vi) Programming Methodology & Software Engineering
(vii)Data Structures and Algorithms
(viii) Database Systems
(ix) Computer Networks
Chemical (Code 07)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Chemical process calculations
(ii) Chemical Process Industries
(iii) Mechanical Operations
(iv) Fluid Mechanics
(v) Heat Transfer
(vi) Mass Transfer
(vii) Thermodynamics
(viii) Chemical Reaction Engineering
(ix) Instrumentation & Control
(x) Process Engineering Economics
Bio Technology (Code 08)
Bio Technology (Code 08)
(i) Cell Structure, Function
(ii) Properties of Nucleic Acids, Protein Synthesis
(iii) Gene Manipulation, Transgenic Microbes
(iv) Plants and Animals
(v) Metabolism and Bio Energetic
(vi) Gene Regulation
(vii) Enzyme Kinetics, Fermentation Process, Production of commercially important enzymes
(viii) Recombinant proteins
(ix) Microbial Growth Kinetics
(x) Biosaftey, Bioethics and Intellectual Property Rights
(xi) Bio conversion
(xii) Fermentation Kinetics, Bioreactors
(xiii) Genomics and Proteomics
(xiv) Computer Applications in Bio Technology
(xv)Nano Biotechnology
(xvi) Application of Bio Technology Systems Biotechnology
GIS (Code 09)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Remote sensing: physics of remote sensing
(ii) Photogrammetry: Photogrammetry
(iii) Surveying: Surveying Techniques
(iv) Electronic surveying
(v) GIS: Terminology
(vi) Geology: Geological Remote Sensing
(vii)Agriculture and forestry
(viii) Environment and disaster studies: EIA
(ix) Urban and regional planning: Urban Planning
Environmental (Code 10)
Mathematics
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics
(i) Environmental Pollution
(ii) Environmental Biotechnology
(iii) Thermodynamics
(iv) Ecology
(v) Environmental Conservation
(vi) Water Resources
(vii) Ecology and Sustainable Development
(viii) Remote Sensing
(ix) Energy and Environmental
(x) Environmental Impact Assessment
(xi) Current Topics in Environmental Sciences
(xii) Soil Pollution and Solid Waste Management
(xiii) Natural Hazards
(xiv) Environmental and Occupational Health
Food Processing (Code 11)
(i) Bioprocess Engineering: Properties of Vapors and Gases. Energy Balances/Conservation of
Energy; Entropy; Ideal Gas Mixtures and Psychometrics. Steady-state Heat Transfer; Onedimensional
Heat Conduction; Heat Transfer through a Composite Wall; Conduction, Forced
Convection; Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient; Heat Exchangers; Radiation Heat Transfer.
Basic bioprocess engineering and reactor concepts; Stoichiometry , mass and energy
balances; Fluid flow and mixing in bioreactors; Heat transfer in bioprocesses; Mass transfer
in bioprocess; Reaction and cell growth kinetics; Downstream processing unit operations.
Process instrumentation
(ii) Food Engineering: Dimensions and units, Evaporation, crystallization, distillation, mechanical
separations, size reduction and mixing, properties of food, blanching, pasteurization,
sterilization, extrusion, aseptic processing, drying, material handling, dairy plant engineering,
cereal processing, fat and oil processing, sugar cane processing, food preservation, storage,
non-thermal food processing, bakery and confectionary, meat and poultry processing, Food
safety and waste management, food packaging technology
(iii) Biochemistry and nutrition: Enzymes, Coenzymes, Cofactors, Elements of carbohydrates, fat
and protein metabolism, Elements of photosynthesis, Food Requirements, Vitamins and
their functions in the body, Minerals and their functions in body, Elements in protein
biosynthesis-Nucleic acids and their importance.
(iv) Microbiology: Microorganism, isolation of microorganism, identification, stains and staining
techniques, Growth, nutrition and physiology of microorganism, diseases and control,
microbial genetics, microbial spoilage in food, beneficial microorganism, probiotic and
prebiotic. Fermentation-Process, types, design, Fermented food products. Enzymesproduction-primary
and secondary metabolites, application in food industry.
Materials Science (Code 12)
MATHEMATICS:
(i) Vector calculus
(ii) Determinants and Matrices
(iii) Analytic function theory
(iv) Differential Calculus, Multiple Integrals and ordinary Differential Equations
(v) Numerical Methods
(vi) Probability and Statistics
Other Topics:
(i) QUANTUM MECHANICS, ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR PHYSICS : Black body radiation,
photoelectric effect – wave-particle duality of radiation– de-Broglie hypothesis of matter
waves – Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle – Schrödinger’s wave equation – physical
interpretation of wave function-Eigen-values and Eigen-functions –particle in a box-simple
harmonic oscillator-Motion in a central potential-orbital angular momentum–particle in a
square-well potential – potential barrier-Spectra of one and many electron atoms-LS and jj
coupling – fine structure – spectroscopic terms and selection rules – hyperfine structure –
exchange symmetry of wave function –Pauli’s exclusion principle-Zeeman and Stark effectsX-ray
– Auger transitions – Compton Effect-basic principles-rotational and vibrational spectra
of diatomic molecules-electronic transition in diatomic molecules-Franck-Condon principleRaman
effect-NMR-ESR-Nuclear properties and forces– radioactivity – alpha, beta and
gamma radiation.
(ii) SOLID STATE PHYSICS: Crystal structure , Bravais lattices and its basis, Miller indices- Crystal
symmetry, point group and space group elements – crystal diffraction and reciprocal latticeelementary
ideas about point defects and dislocations (edge and screw) – Physical
Properties of materials – lattice vibrations, phonons – specific heat of solids – thermal and
electrical conductivity – Di-electrics behavior – Polarization mechanisms, Clausius-Mossotti
equation, Piezo, Pyro and ferro electricity- free electron theory of metals- Fermi energy and
density of states- Energy levels in One Dimension, Fermi-Dirac Distribution, effect of
Temperature on the Fermi-Dirac Distribution, free electron Gas in Three Dimension-origin of
energy bands- Elements of band theory – Electrons motion in periodic potential, concept of
holes and effective mass- Hall effect- Different types of materials: Metals, Semiconductors,
Composite materials, Ceramics, Alloys, Polymers
(iii) LASERS: Basic Principle of Laser- Threshold condition-Einstein Coefficients – condition for
light amplification – – Line shape function – Optical Resonators -CW operation of laser; Critical
pumping rate- Population inversion and photon number in the cavity around threshold;
Output coupling of laser power- Optical resonators- Cavity modes- Three level and four level
systems. Solid State lasers – Ruby and Nd-YAG Laser – Gas lasers – He-Ne and Co2 lasers –
semiconductor lasers – Heterojunction lasers – Liquid Dye lasers – Qswitching and mode
locking. Application of laser in industry-Medical applications -Holography – Theory of
recording and reconstruction – application of Holography
(iv) ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM: Electrostatics; Coulomb’s law, Gauss’s law and its
applications, Laplace and Poisson equations, boundary conditions Conductors, capacitors,
dielectrics, dielectric polarization, volume and surface charges, electrostatic energy,
Magnetostatics, Biot-Savart law, Ampere’s law, Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction,
Maxwell’s equations and static and time varying equations, Poynting theorem Lorentz Force
and motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields, energy and momentum of
electromagnetic waves, radiation from a moving charge. Electromagnetic waves in free
space, dielectrics, and conductors, Reflection and refraction, polarization, Fresnel’s Law,
interference, coherence, and diffraction, Dia, Para and Ferromagnetism, Langevin’s theory of
paramagnetism
(v) THERMODYNAMICS: Thermodynamic system – Path and Process – Zeroth law of
Thermodynamics – Concept of Temperature – First law of Thermodynamics – Isothermal and
Adiabatic Processes – Second law of Thermodynamics – Reversible and Irreversible
processes – Carnot’s Engine – Thermodynamic Substance of Pure Substances – Kinetic
Theory of gases – Law of Equipartition Energy – Ideal and Real Gases – Equation of State –
Thermodynamic relation – T-ds relation – Maxwell’s Equation – Phase Transitions – Gibbs’s
Phase Rule – Van’t Hoff’s Equation
(vi) MATERIALS CHEMISTRY: Atomic structure – Bohr’s theory – Exclusion principle – Hund’s
rule – Afbau principle – Periodic law and arrangement of elements – Bonding structure –
Ionic, Covalent, Metallic, Weak bonds- Acids and Bases- Chemical periodicity – Structure and
bonding in homo- and heteronuclear molecules (VSEPR Theory) – Allotropes of carbon:
graphite, diamond, C60. Synthesis and reactivity of inorganic polymers of Si and P –
Hydrocarbons – IUPAC Nomenclature – Hybridization – Aromaticity – Huckel’s rule –
Tautomerism – Stereochemistry – Electrochemistry – Electrochemical cells; standard
electrode potentials: applications – corrosion and energy conversion
(vii)BIOLOGY AND HEALTH SCIENCES Anatomy: Cardiovascular System-Respiratory SystemExcretory
System. Physiology: Chemical composition of the body -Neurons & membrane
potentials. Basic Cell biology: Cell components- Cell membrane structure- DNA structure.
Genetics: DNA replication-transcription and translation-Bacteriology: Bacterial cell- structure
and function. Virology: Bacteriophage-Microbes- Types. Common infectious diseases:
Hepatitis, Malaria, HIV/AIDS. Cancers: Types and Classification. Biochemistry: Amino acidsCarbohydrates-
Lipids. Immunology: components and response to foreign body
(viii) ELECTRONICS: Semiconductors: Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, Fermi level, P-N
junction diodes-Bipolar junction transistors and its applications, field effect transistors, JFET,
MOSFET, MESFET, MODFET and CCD: Various structures and their functioning, I-V
characteristic studies and applications, Transistor circuits in CE, CB, CC modes, Amplifier
circuits with transistors-Operational amplifier and its applications: Inverting, non -inverting,
adder, sub tractor, differentiator, wave form generator, comparator, filters (LPF, BPF, HPF),
Schmitt trigger, the 555 timer -Gates, flip flops, switches, registers, counters,
multivibrators, principles of A/D and D/A converters, applications of A/D and D/A
Converters, Regulators-CMOS process technology: silicon –semiconductor technology,
wafer processing, oxidation, epitaxial, deposition, ion implantation and diffusion, n-well
CMOS process, p-well CMOS process, Twin tub CMOS process and silicon on insulator
(ix) MEMS/NEMS: Top down approach- front end approach-MEMS materials-MEMS
Fabrication Techniques :Bulk micromachining , Surface micromachining, Micro-molding
processes, Non-lithography based localized micromachining- Applications of MEMS/NEMSMechanical
Transducers : transduction methods, accelerometers, gyroscopes ,pressure
sensors-Design, Scaling Properties/Issues- Chemical and Biological Transducers: chemical
sensors, molecule based biosensors, cell based biosensors, chemical actuators, biological
transducers, and electrophoresis- optical transducers- thermal transducers-magnetic
transducers-RF transducers- Characterization of Micro/Nano Electromagnetic Mechanical
Systems.
SRMJEE MTech sample questions:
A Questions paper containing about 100 sample questions for SRMJEE post graduation is given below:
Download the sample paper here.
Download the answer key here